Introduction
The SENSEX, short for the Bombay Stock Exchange Sensitive Index, is one of India’s most important stock market indices. It represents the performance of 30 of the largest and most actively traded stocks on the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE). This comprehensive guide will cover everything you need to know about the SENSEX, including its history, composition, significance, and how to track its movements.
What is the SENSEX?
The SENSEX, also known as the BSE 30, is a free-float market-weighted stock market index of 30 well-established and financially sound companies listed on the BSE. These companies represent various sectors of the Indian economy, making the BSE SENSEX a barometer of India’s overall market sentiment and economic health.
History of the SENSEX
The SENSEX has a rich history that dates back several decades:
- 1986: The BSE compiled and published the SENSEX on January 1, 1986. It was introduced to provide investors with a benchmark to track the performance of the Indian stock market.
- 1990s: The SENSEX gained prominence as the Indian economy opened up and foreign investments started flowing in.
- 2000s: The index saw significant growth with the boom in the IT and services sectors, reflecting India’s rapid economic expansion.
- 2010s: The SENSEX continued to grow, hitting new milestones as India’s economy diversified and matured.
Composition of the SENSEX
SENSEX comprises 30 of the largest and most liquid stocks listed on the BSE. These companies are selected based on several criteria, including market capitalization, liquidity, revenue, and sector representation. The index is reviewed periodically to ensure it reflects the current market conditions.
Key Companies in the SENSEX
Some of the prominent companies included in the BSE SENSEX are:
- Reliance Industries
- Tata Consultancy Services (TCS)
- HDFC Bank
- Infosys
- ICICI Bank
- Hindustan Unilever
- State Bank of India (SBI)
- Bharti Airtel
- Larsen & Toubro (L&T)
Significance of the SENSEX
The SENSEX is a crucial indicator for several reasons:
1. Economic Indicator
- SENSEX serves as a barometer of the Indian economy. A rising SENSEX indicates investor confidence and a growing economy, while a falling SENSEX signals economic challenges.
2. Investment Benchmark
- Investors use the SENSEX as a benchmark to gauge the performance of their investments. Mutual funds and portfolio managers compare their returns against the SENSEX to evaluate their performance.
3. Market Sentiment
- The movements of the SENSEX reflect the overall market sentiment. Positive news, such as strong corporate earnings or favorable government policies, can drive the SENSEX up, while negative news, such as political instability or economic downturns, can pull it down.
How the SENSEX is Calculated?
The SENSEX is calculated using the free-float market capitalization method. This method considers only the shares that are readily available for trading in the market, excluding promoters’ holdings and other restricted shares. The formula for calculating the SENSEX is:
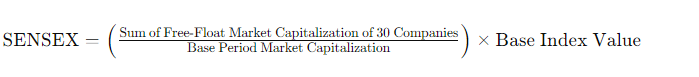 The base year for the SENSEX is 1978-79, and the base value is 100.
The base year for the SENSEX is 1978-79, and the base value is 100.
Tracking the SENSEX
Investors can track the SENSEX through various mediums:
- Financial News Websites: Websites like Moneycontrol, Bloomberg, and Reuters provide real-time updates and comprehensive analysis of the SENSEX.
- Stock Market Apps: Mobile apps such as BSE India, NSE Mobile Trading, and Zerodha Kite offer real-time tracking of the SENSEX and other market indices.
- Television Channels: Financial news channels like CNBC TV18, ET Now, and Bloomberg Quint provide live coverage and expert analysis of the SENSEX.
- BSE Website: The official BSE website (www.bseindia.com) provides real-time data, historical data, and detailed information about the SENSEX and its constituent companies.
Factors Influencing the SENSEX
Several factors influence the SENSEX, which in turn affects the overall market sentiment.
Here are the key factors that influence the movements of the SENSEX:
1. Economic Indicators
Economic data such as GDP growth rate, inflation, industrial production, and employment figures play a crucial role in determining the direction of the SENSEX.
Influence:
- Positive Economic Growth: Higher GDP growth rates and favorable economic conditions generally lead to a bullish market, pushing the SENSEX higher.
- Rising Inflation: High inflation can reduce consumer purchasing power, leading to lower corporate profits, which may negatively impact the SENSEX.
2. Corporate Earnings
The financial performance of the companies listed on the BSE, particularly those in the SENSEX, significantly influences the index.
Influence:
- Strong Earnings Reports: If major companies report strong earnings, it boosts investor confidence and drives the SENSEX upwards.
- Weak Earnings: Conversely, disappointing corporate earnings can lead to a decline in the SENSEX as investors adjust their expectations.
3. Global Market Trends
The SENSEX is influenced by global financial markets, including major indices like the Dow Jones, NASDAQ, FTSE, and Nikkei.
Influence:
- Global Market Rallies: Positive performance in global markets often leads to an optimistic outlook in the Indian market, boosting the SENSEX.
- Global Economic Uncertainty: Global events such as geopolitical tensions, economic crises, or changes in foreign trade policies can negatively impact the SENSEX.
4. Interest Rates
Interest rate changes by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) affect borrowing costs and overall economic activity.
Influence:
- Lower Interest Rates: When the RBI lowers interest rates, it reduces the cost of borrowing, encouraging investment and spending, which can lead to a rise in the SENSEX.
- Higher Interest Rates: Conversely, higher interest rates can slow down economic growth, leading to a decline in the SENSEX.
5. Foreign Institutional Investors (FII) Activity
The buying and selling activities of Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) have a significant impact on the SENSEX.
Influence:
- FII Inflows: A large influx of funds from FIIs into Indian equities generally leads to a rise in the SENSEX.
- FII Outflows: On the other hand, when FIIs withdraw their investments, it can lead to a decline in the index.
6. Political Stability
Political events and government policies can create uncertainty or confidence in the market.
Influence:
- Stable Government: Political stability and pro-business government policies generally boost investor confidence, positively influencing the SENSEX.
- Political Uncertainty: Political instability or adverse government policies can lead to market volatility and negatively impact the SENSEX.
7. Currency Fluctuations
The value of the Indian Rupee against major currencies like the US Dollar can influence the SENSEX.
Influence:
- Rupee Appreciation: A stronger rupee can reduce the cost of imports and improve the profit margins of companies, leading to a rise in the SENSEX.
- Rupee Depreciation: A weaker rupee can increase costs for companies that rely on imports, negatively affecting their earnings and dragging the SENSEX down.
8. Commodity Prices
Prices of key commodities like crude oil, gold, and other raw materials can impact the costs and profitability of Indian companies.
Influence:
- Rising Commodity Prices: Higher prices for commodities like crude oil can increase input costs for companies, potentially leading to lower profits and a decline in the SENSEX.
- Falling Commodity Prices: Lower commodity prices can reduce costs and improve margins, positively impacting the SENSEX.
You may also want to know about Intraday Trading
BSE SENSEX and Economic Cycles
As of 12 Aug 2024, we can say that the BSE SENSEX, as a barometer of the Indian stock market, is closely linked to the broader economic cycles. Economic cycles, also known as business cycles, are the natural fluctuations in economic activity over time, marked by periods of expansion (growth) and contraction (recession). The SENSEX tends to move in tandem with these cycles, reflecting the overall health of the economy.
Here’s how the SENSEX behaves across different phases of economic cycles:
1. Expansion Phase
During the expansion phase, the economy experiences growth characterized by increasing GDP, rising employment, higher consumer spending, and robust corporate earnings.
Impact on SENSEX:
- Bull Market: As the economy expands, investor confidence grows, leading to higher stock demand. This drives the SENSEX up, often resulting in a bull market.
- Positive Sentiment: Companies typically report strong earnings, further boosting stock prices. The SENSEX tends to reach new highs during this phase.
2. Peak Phase
The peak phase marks the point at which economic growth reaches its maximum rate before slowing down. The economy is performing at its best, but the growth rate decelerates.
Impact on SENSEX:
- Market Plateau: The BSE SENSEX may continue to rise but at a slower pace. Stock prices might reach their highest levels, and market valuations can become stretched.
- Increased Volatility: As the economy shows signs of slowing down, investors may become cautious, leading to increased market volatility.
3. Contraction Phase
In the contraction phase, the economy starts to slow down, marked by decreasing GDP, rising unemployment, reduced consumer spending, and declining corporate profits.
Impact on SENSEX:
- Bear Market: The SENSEX usually declines during this phase as investor sentiment turns negative. Lower corporate earnings and economic uncertainty lead to reduced demand for stocks.
- Negative Sentiment: Stock prices fall, and the SENSEX may experience significant losses, sometimes leading to a bear market.
4. Through Phase
The trough phase represents the lowest point of the economic cycle, where economic activity bottoms out before starting to recover. This phase is characterized by low GDP, high unemployment, and weak consumer confidence.
Impact on SENSEX:
- Market Bottoming: The BSE SENSEX typically reaches its lowest levels during this phase. However, savvy investors might see this as a buying opportunity, anticipating a future recovery.
- Stabilization: As the economy begins to show signs of stabilization, the BSE SENSEX may start to stabilize as well, setting the stage for the next expansion phase.
5. Recovery Phase
The recovery phase follows the trough and marks the beginning of economic growth. GDP starts to rise, unemployment decreases, and consumer and business confidence begin to improve.
Impact on SENSEX:
- Market Rebound: The SENSEX starts to recover as investors gain confidence in the improving economic outlook. Stock prices begin to rise in anticipation of better corporate earnings and stronger economic performance.
- Renewed Optimism: The recovery phase often sets the stage for the next bull market, as the economy gains momentum and growth accelerates.
The SENSEX is generally procyclical, meaning it tends to rise during periods of economic expansion and fall during periods of economic contraction.
The SENSEX is influenced by economic cycles, and it can also act as a leading indicator. It often reacts in advance to anticipated changes in economic conditions. Investors and analysts closely monitor the SENSEX to gauge the future direction of the economy.
How to Invest in SENSEX?
Investors can gain exposure to the BSE SENSEX through various methods:
- Direct Stock Investment: Investors can buy shares of companies included in the SENSEX through a brokerage account. This method requires individual stock selection and active portfolio management.
- Index Funds: Index funds are mutual funds that replicate the performance of the SENSEX by investing in the same companies in the same proportions. These funds offer diversification and are passively managed.
- Exchange-traded funds (ETFs): ETFs that track the SENSEX are traded on stock exchanges like regular stocks. They offer liquidity, diversification, and low management fees.
Conclusion
As of 12, the BSE SENSEX is a critical indicator of the Indian stock market and economy. Its movements reflect investor sentiment, economic conditions, and corporate performance. By staying updated on the BSE SENSEX indices, investors can make profitable decisions and better navigate the complexities of the stock market.










